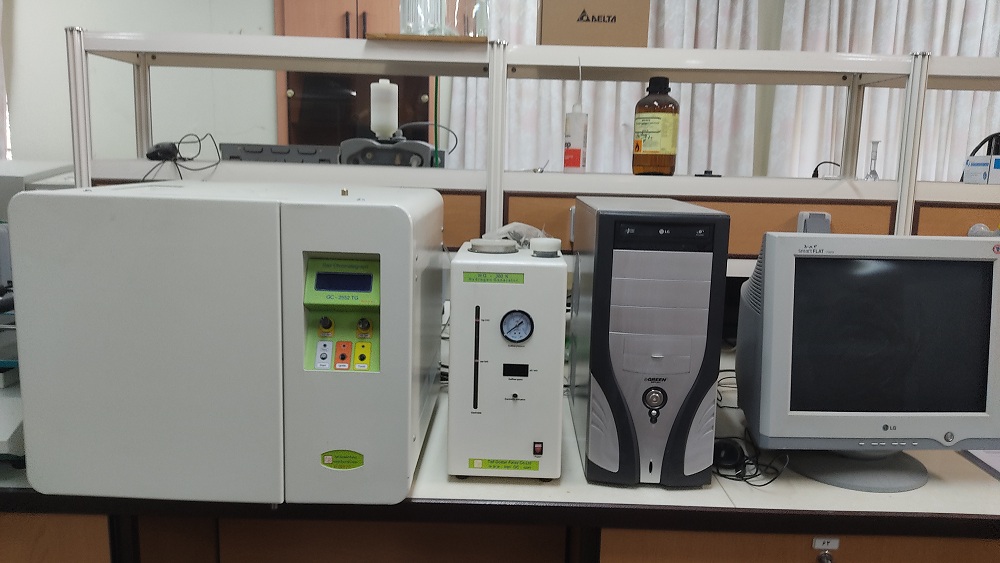
GC-2550 TG Gas Chromatograph
Specification:
| High speed (32 Hz) High resolution (24 Bit) High quality EPC gas control for capillary column inlet pressure control (Optional) MFC gas control for split setting. 6 more MFC Chanel available in software Same time analyze of FID and TCD |
| Low price and excellent after sale service and guaranty |
Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition. Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, or separating the different components of a mixture. Gas chromatography is also sometimes known as vapor-phase chromatography (VPC), or gas–liquid partition chromatography (GLPC). These alternative names, as well as their respective abbreviations, are frequently used in scientific literature.
A gas chromatograph (GC) is an analytical instrument that measures the content of various components in a sample. The analysis performed by a gas chromatograph is called gas chromatography. Principle of gas chromatography: The sample solution injected into the instrument enters a gas stream which transports the sample into a separation tube known as the "column." (Helium or nitrogen is used as the so-called carrier gas.) The various components are separated inside the column. The detector measures the quantity of the components that exit the column. To measure a sample with an unknown concentration, a standard sample with known concentration is injected into the instrument. The standard sample peak retention time (appearance time) and area are compared to the test sample to calculate the concentration.
Advantages of gas chromatography:
1) High separation efficiency and analysis speed: for example, gasoline samples can obtain more than 200
chromatographic peaks in 2 hrs. A general sample analysis can be completed in 20 minutes.
2) Small sample consumption and high detection sensitivity: 1 ml of gas sample consumption, 0.1 µl of
liquid sample consumption, a few mg of solid sample consumption. Proper detectors can detect impurities
in the tens to a few parts per million.
3) Gas chromatography has good selectivity and can be used to analyze aze tropic mixtures and samples
with close boiling points. For example, some isotopes, cis-trans isomers, adjacent or intertrans isomers,
optical isomers, etc.
4) Wide range of applications, although mainly used to analyze gases and volatile organic substances
under certain conditions, it can also be used to analyze high boiling point substances and solid samples.
Disadvantages of gas chromatography
It can only be used to analyze volatile substances. Some highly polar substances can be derived
to increase their volatility for GC analysis, but the process can be complex and may introduce
errors in quantitative analysis.